Catalog Maintenance¶
Catalog Database¶
Bareos stores its catalog in a database. Different database backends are offered:
- PostgreSQL (recommended)
- MariaDB/MySQL (see MySQL/MariaDB Support)
- Sqlite (only for testing)
What database will be used, can be configured in the Bareos Director configuration, see the Catalog Resource.
The database often runs on the same server as the Bareos Director. However, it is also possible to run it on a different system. This might require some more manual configuration, a PostgreSQL example can be found in Remote PostgreSQL Database.
dbconfig-common (Debian)¶
Since Bareos Version >= 14.2.0 the Debian (and Ubuntu) based packages support the dbconfig-common mechanism to create and update the Bareos database, according to the user choices.
The first choice is, if dbconfig-common should be used at all. If you decide against it, the database must be configured manually, see Manual Configuration.
If you decided to use dbconfig-common, the next question will only be asked, if more than one Bareos database backend (bareos-database-*) is installed. If this is the case, select the database backend you want to use.
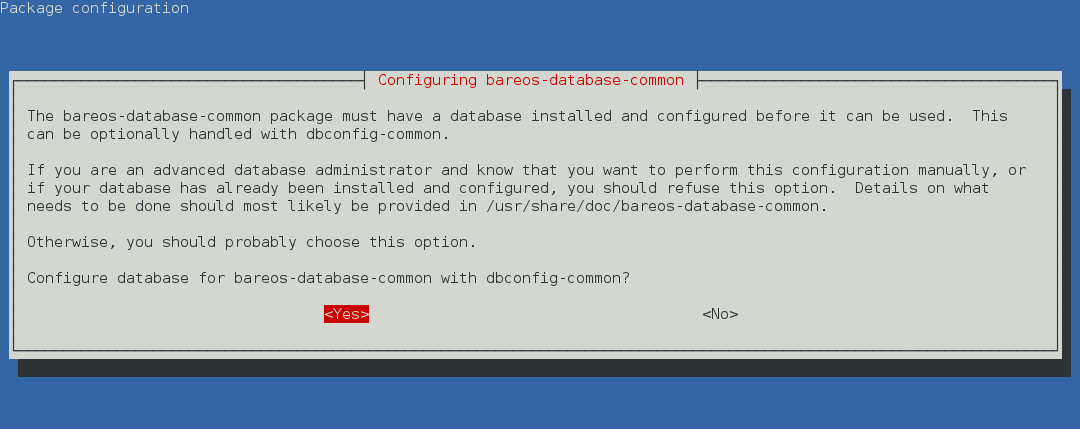
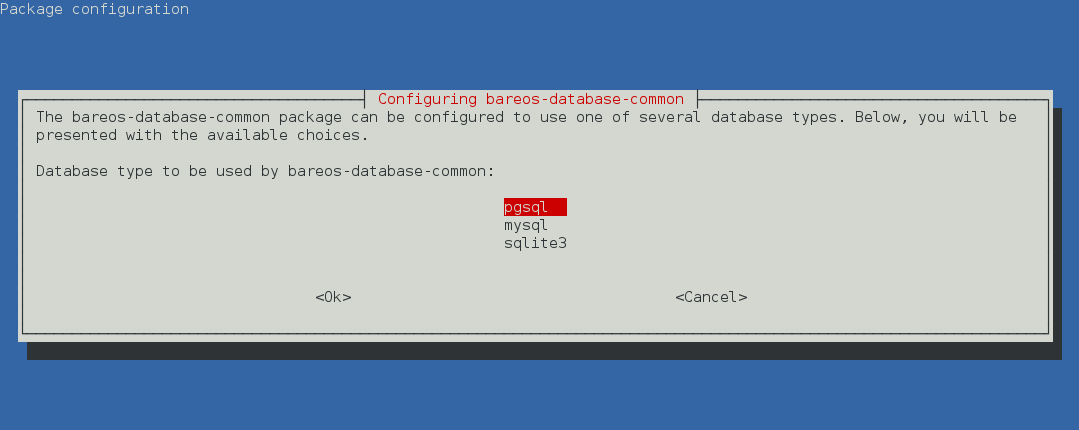
Depending on the selected database backend, more questions about how to access the database will be asked. Often, the default values are suitable.
The dbconfig-common configuration (and credentials) is done by the bareos-database-common package. Settings are stored in the file /etc/dbconfig-common/bareos-database-common.conf.
The Bareos database backend will get automatically configured in /etc/bareos/bareos-dir.d/catalog/MyCatalog.conf. If the Server is not running locally you need to specify DB Address (Dir->Catalog) in the catalog ressource. A later reconfiguration might require manual adapt changes.
Warning
When using the PostgreSQL backend and updating to Bareos < 14.2.3, it is necessary to manually grant database permissions (grant_bareos_privileges), normally by
<command> </command><parameter>su - postgres -c /usr/lib/bareos/scripts/grant_bareos_privileges</parameter>
For details see chapter Manual Configuration.
Manual Configuration¶
Bareos comes with a number of scripts to prepare and update the databases. All these scripts are located in the Bareos script directory, normally at /usr/lib/bareos/scripts/.
| Script | Stage | Description |
|---|---|---|
create_bareos_database |
installation | create Bareos database |
make_bareos_tables |
installation | create Bareos tables |
grant_bareos_privileges |
installation | grant database access privileges |
update_bareos_tables [-f] |
update | update the database schema |
drop_bareos_tables |
deinstallation | remove Bareos database tables |
drop_bareos_database |
deinstallation | remove Bareos database |
make_catalog_backup.pl |
backup | backup the Bareos database, default on Linux |
make_catalog_backup |
backup | backup the Bareos database for systems without Perl |
delete_catalog_backup |
backup helper | remove the temporary Bareos database backup file |
The database preparation scripts have following configuration options:
- db_type
- command line parameter $1
DB Driver (Dir->Catalog)from the configuration- installed database backends
- fallback: postgresql
- db_name
- environment variable
db_name DB Name (Dir->Catalog)from the configuration- default: bareos
- environment variable
- db_user
- environment variable
db_user DB User (Dir->Catalog)from the configuration- default: bareos
- environment variable
- db_password
- environment variable
db_password DB Password (Dir->Catalog)from the configuration- default: none
- environment variable
Reading the settings from the configuration require read permission for the current user. The normal PostgreSQL administrator user (postgres) don’t have these permissions. So if you plan to use non-default database settings, you might add the user postgres to the group bareos.
The database preparation scripts need to have password-less administrator access to the database. Depending on the distribution you’re using, this require additional configuration. See the following section about howto achieve this for the different database systems.
To view and test the currently configured settings, use following commands:
<command> </command><parameter>/usr/sbin/bareos-dbcheck -B</parameter>
catalog=MyCatalog
db_name=bareos
db_driver=mysql
db_user=bareos
db_password=YourPassword
db_address=
db_port=0
db_socket=
db_type=MySQL
working_dir=/var/lib/bareos
<command> </command><parameter>/usr/sbin/bareos-dir -t -f -d 500</parameter>
[...]
bareos-dir: mysql.c:204-0 Error 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'bareos'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
bareos-dir: dird.c:1114-0 Could not open Catalog "MyCatalog", database "bareos".
bareos-dir: dird.c:1119-0 mysql.c:200 Unable to connect to MySQL server.
Database=bareos User=bareos
MySQL connect failed either server not running or your authorization is incorrect.
bareos-dir: mysql.c:239-0 closedb ref=0 connected=0 db=0
25-Apr 16:25 bareos-dir ERROR TERMINATION
Please correct the configuration in /etc/bareos/bareos-dir.d/*/*.conf
PostgreSQL configuration¶
On most distributions, PostgreSQL uses ident to allow access to the database system. The database administrator account is the Unix user postgres. Normally, this user can access the database without password, as the ident mechanism is used to identify the user.
If this works on your system can be verified by
su - postgres
psql
If your database is configured to require a password, this must be definied in the file :file:`~/.pgpass <http://www.postgresql.org/docs/8.2/static/libpq-pgpass.html>`_ in the following syntax: HOST:PORT:DATABASE:USER:PASSWORD, e.g.
localhost:*:bareos:bareos:secret
The permission of this file must be 0600 (chmod 0600 ~/.pgpass).
Again, verify that you have specified the correct settings by calling the psql command. If this connects you to the database, your credentials are good. Exit the PostgreSQL client and run the Bareos database preparation scripts:
su - postgres
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/create_bareos_database
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/make_bareos_tables
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/grant_bareos_privileges
The encoding of the bareos database must be SQL_ASCII. The command create_bareos_database automatically creates the database with this encoding. This can be verified by the command psql -l, which shows information about existing databases:
<command>psql</command><parameter> -l</parameter>
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding
-----------+----------+-----------
bareos | postgres | SQL_ASCII
postgres | postgres | UTF8
template0 | postgres | UTF8
template1 | postgres | UTF8
(4 rows)
The owner of the database may vary. The Bareos database maintance scripts don’t change the default owner of the Bareos database, so it stays at the PostgreSQL administration user. The grant_bareos_privileges script grant the required permissions to the Bareos database user. In contrast, when installing (not updating) using dbconfig, the database owner will be identical with the Bareos database user.
By default, using PostgreSQL ident, a Unix user can access a database of the same name. Therefore the user bareos can access the database bareos.
root@linux:~# <input>su - bareos -s /bin/sh</input>
bareos@linux:~# <input>psql</input>
Welcome to psql 8.3.23, the PostgreSQL interactive terminal.
Type: \copyright for distribution terms
\h for help with SQL commands
\? for help with psql commands
\g or terminate with semicolon to execute query
\q to quit
bareos=> <input>\dt</input>
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------------------+-------+----------
public | basefiles | table | postgres
public | cdimages | table | postgres
public | client | table | postgres
public | counters | table | postgres
public | device | table | postgres
public | devicestats | table | postgres
public | file | table | postgres
public | filename | table | postgres
public | fileset | table | postgres
public | job | table | postgres
public | jobhisto | table | postgres
public | jobmedia | table | postgres
public | jobstats | table | postgres
public | location | table | postgres
public | locationlog | table | postgres
public | log | table | postgres
public | media | table | postgres
public | mediatype | table | postgres
public | ndmpjobenvironment | table | postgres
public | ndmplevelmap | table | postgres
public | path | table | postgres
public | pathhierarchy | table | postgres
public | pathvisibility | table | postgres
public | pool | table | postgres
public | quota | table | postgres
public | restoreobject | table | postgres
public | status | table | postgres
public | storage | table | postgres
public | unsavedfiles | table | postgres
public | version | table | postgres
(30 rows)
bareos=> <input>select * from Version;</input>
versionid
-----------
2002
(1 row)
bareos=> <input>\du</input>
List of roles
Role name | Superuser | Create role | Create DB | Connections | Member of
---------------+-----------+-------------+-----------+-------------+-----------
bareos | no | no | no | no limit | {}
postgres | yes | yes | yes | no limit | {}
(2 rows)
bareos=> <input>\dp</input>
Access privileges for database "bareos"
Schema | Name | Type | Access privileges
--------+-----------------------------------+----------+--------------------------------------
public | basefiles | table | {root=arwdxt/root,bareos=arwdxt/root}
public | basefiles_baseid_seq | sequence | {root=rwU/root,bareos=rw/root}
...
bareos=>
Remote PostgreSQL Database¶
When configuring bareos with a remote database, your first step is to check the connection from the Bareos Director host into the database. A functional connection can be verified by
su - postgres
psql --host bareos-database.example.com
With a correct configuration you can access the database, if it fails you need to correct the PostgreSQL servers configuration files.
One way to manually create the database would be calling the bareos database preparation scripts with the –host option, explained later. How ever, it is advised to use the dbconfig-common. Both methods require you to add the database hostname/address as DB Address (Dir->Catalog).
If you’re using dbconfig-common you should choose New Host, enter the hostname or the local address followed by the password. As dbconfig-common uses the ident authentication by default the first try to connect will fail. Don’t be bothered by that. Choose Retry when prompted. From there, read carefully and configure the database to your needs. The authentication should be set to password, as the ident method will not work with a remote server. Set the user and administrator according to your PostgreSQL servers settings.
Set the PostgreSQL server IP as DB Address (Dir->Catalog) in Catalog Resource. You can also customize other parameters or use the defaults. A quick check should display your recent changes:
<command> </command><parameter>/usr/sbin/bareos-dbcheck -B</parameter>
catalog=MyCatalog
db_name=bareos
db_driver=postgresql
db_user=bareos
db_password=secret
db_address=bareos-database.example.com
db_port=0
db_socket=
db_type=PostgreSQL
working_dir=/var/lib/bareos
If dbconfig-common did not succeed or you choosed not to use it, run the Bareos database preparation scripts with:
su - postgres
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/create_bareos_database --host=bareos-database.example.com
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/make_bareos_tables --host=bareos-database.example.com
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/grant_bareos_privileges --host=bareos-database.example.com
MySQL¶
MySQL user authentication is username, password and host-based. The database administrator is the user root.
On some distributions access to the MySQL database is allowed password-less as database user root, on other distributions, a password is required. On productive systems you normally want to have password secured access.
The bareos database preparation scripts require password-less access to the database. To guarantee this, create a MySQL credentials file :file:`~/.my.cnf <http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/4.1/en/password-security.html>`_ with the credentials of the database administrator:
[client]
host=localhost
user=root
password=<input>YourPasswordForAccessingMysqlAsRoot</input>
Alternatively you can specifiy your database password by adding it to the file /etc/my.cnf.
Verify that you have specified the correct settings by calling the mysql command. If this connects you to the database, your credentials are good. Exit the MySQL client.
For the Bareos database connection, you should specify a database password. Otherwise the Bareos database user gets the permission to connect without password. This is not recommended. Choose a database password and add it into the Bareos Director configuration file /etc/bareos/bareos-dir.conf:
After this, run the Bareos database preparation scripts. For Bareos <= 13.2.2, the database password must be specified as environment variable db_password. From Version >= 13.2.3 the database password is read from the configuration, if no environment variable is given.
export db_password=<input>YourSecretPassword</input>
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/create_bareos_database
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/make_bareos_tables
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/grant_bareos_privileges
After this, you can use the mysql command to verify that your database setup is okay and works with your the Bareos database user. The result should look similar as this (here Bareos 13.2 is used on SLES11):
root@linux:~# <input>mysql --user=bareos --password=YourSecretPassword bareos</input>
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 162
Server version: 5.5.32 SUSE MySQL package
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> <input>show tables;</input>
+--------------------+
| Tables_in_bareos |
+--------------------+
| BaseFiles |
| CDImages |
| Client |
| Counters |
| Device |
| DeviceStats |
| File |
| FileSet |
| Filename |
| Job |
| JobHisto |
| JobMedia |
| JobStats |
| Location |
| LocationLog |
| Log |
| Media |
| MediaType |
| NDMPJobEnvironment |
| NDMPLevelMap |
| Path |
| PathHierarchy |
| PathVisibility |
| Pool |
| Quota |
| RestoreObject |
| Status |
| Storage |
| UnsavedFiles |
| Version |
+--------------------+
30 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> <input>describe Job;</input>
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| JobId | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| Job | tinyblob | NO | | NULL | |
| Name | tinyblob | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| Type | binary(1) | NO | | NULL | |
| Level | binary(1) | NO | | NULL | |
| ClientId | int(11) | YES | | 0 | |
| JobStatus | binary(1) | NO | | NULL | |
| SchedTime | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| StartTime | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| EndTime | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| RealEndTime | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| JobTDate | bigint(20) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| VolSessionId | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| VolSessionTime | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| JobFiles | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| JobBytes | bigint(20) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| ReadBytes | bigint(20) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| JobErrors | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| JobMissingFiles | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| PoolId | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| FileSetId | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| PriorJobId | int(10) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
| PurgedFiles | tinyint(4) | YES | | 0 | |
| HasBase | tinyint(4) | YES | | 0 | |
| HasCache | tinyint(4) | YES | | 0 | |
| Reviewed | tinyint(4) | YES | | 0 | |
| Comment | blob | YES | | NULL | |
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
27 rows in set (0,00 sec)
mysql> <input>select * from Version;</input>
+-----------+
| VersionId |
+-----------+
| 2002 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> <input>exit</input>
Bye
Modify database credentials¶
If you want to change the Bareos database credentials, do the following:
- stop the Bareos director
- modify the configuration
- rerun the grant script grant_bareos_privileges (or modify database user directly)
- start the Bareos director
Modify the configuration, set a new password:
Rerun the Bareos grant script grant_bareos_privileges …
export db_password=<input>MyNewSecretPassword</input>
/usr/lib/bareos/scripts/grant_bareos_privileges
Sqlite¶
There are different versions of Sqlite available. When we use the term Sqlite, we will always refer to Sqlite3.
Sqlite is a file based database. Access via network connection is not supported. Because its setup is easy, it is a good database for testing. However please don’t use it in a production environment.
Sqlite stores a database in a single file. Bareos creates this file at /var/lib/bareos/bareos.db.
Sqlite does not offer access permissions. The only permissions that do apply are the Unix file permissions.
The database is accessable by following command:
<command>sqlite3</command><input> /var/lib/bareos/bareos.db</input>
SQLite version 3.7.6.3
Enter ".help" for instructions
Enter SQL statements terminated with a ";"
sqlite> <input>.tables</input>
BaseFiles Filename Media Pool
CDImages Job MediaType Quota
Client JobHisto NDMPJobEnvironment RestoreObject
Counters JobMedia NDMPLevelMap Status
Device JobStats NextId Storage
DeviceStats Location Path UnsavedFiles
File LocationLog PathHierarchy Version
FileSet Log PathVisibility
sqlite> <input>select * from Version;</input>
2002
sqlite>
Retention Periods¶
Database Size¶
As mentioned above, if you do not do automatic pruning, your Catalog will grow each time you run a Job. Normally, you should decide how long you want File records to be maintained in the Catalog and set the File Retention period to that time. Then you can either wait and see how big your Catalog gets or make a calculation assuming approximately 154 bytes for each File saved and knowing the number of Files that are saved during each backup and the number of Clients you backup.
For example, suppose you do a backup of two systems, each with 100,000 files. Suppose further that you do a Full backup weekly and an Incremental every day, and that the Incremental backup typically saves 4,000 files. The size of your database after a month can roughly be calculated as:
Size = 154 * No. Systems * (100,000 * 4 + 10,000 * 26)
where we have assumed four weeks in a month and 26 incremental backups per month. This would give the following:
Size = 154 * 2 * (100,000 * 4 + 10,000 * 26) = 203,280,000 bytes
So for the above two systems, we should expect to have a database size of approximately 200 Megabytes. Of course, this will vary according to how many files are actually backed up.
You will note that the File table (containing the file attributes) make up the large bulk of the number of records as well as the space used. As a consequence, the most important Retention period will be the File Retention period.
Without proper setup and maintenance, your Catalog may continue to grow indefinitely as you run Jobs and backup Files, and/or it may become very inefficient and slow. How fast the size of your Catalog grows depends on the number of Jobs you run and how many files they backup. By deleting records within the database, you can make space available for the new records that will be added during the next Job. By constantly deleting old expired records (dates older than the Retention period), your database size will remain constant.
Setting Retention Periods¶
Bareos uses three Retention periods: the File Retention period, the Job Retention period, and the Volume Retention period. Of these three, the File Retention period is by far the most important in determining how large your database will become.
The File Retention and the Job Retention are specified in each Client resource as is shown below. The Volume Retention period is specified in the Pool resource, and the details are given in the next chapter of this manual.
- File Retention = <time-period-specification>
The File Retention record defines the length of time that Bareos will keep File records in the Catalog database. When this time period expires, and if AutoPrune is set to yes, Bareos will prune (remove) File records that are older than the specified File Retention period. The pruning will occur at the end of a backup Job for the given Client. Note that the Client database record contains a copy of the File and Job retention periods, but Bareos uses the current values found in the Director’s Client resource to do the pruning.
Since File records in the database account for probably 80 percent of the size of the database, you should carefully determine exactly what File Retention period you need. Once the File records have been removed from the database, you will no longer be able to restore individual files in a Job. However, as long as the Job record still exists, you will be able to restore all files in the job.
Retention periods are specified in seconds, but as a convenience, there are a number of modifiers that permit easy specification in terms of minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, quarters, or years on the record. See the Configuration chapter of this manual for additional details of modifier specification.
The default File retention period is 60 days.
- Job Retention = <time-period-specification>
The Job Retention record defines the length of time that Bareos will keep Job records in the Catalog database. When this time period expires, and if AutoPrune is set to yes Bareos will prune (remove) Job records that are older than the specified Job Retention period. Note, if a Job record is selected for pruning, all associated File and JobMedia records will also be pruned regardless of the File Retention period set. As a consequence, you normally will set the File retention period to be less than the Job retention period.
As mentioned above, once the File records are removed from the database, you will no longer be able to restore individual files from the Job. However, as long as the Job record remains in the database, you will be able to restore all the files backuped for the Job. As a consequence, it is generally a good idea to retain the Job records much longer than the File records.
The retention period is specified in seconds, but as a convenience, there are a number of modifiers that permit easy specification in terms of minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, quarters, or years. See the Configuration chapter of this manual for additional details of modifier specification.
The default Job Retention period is 180 days.
Auto Prune (Dir->Client)- If set to yes, Bareos will automatically apply the File retention period and the Job retention period for the Client at the end of the Job. If you turn this off by setting it to no, your Catalog will grow each time you run a Job.
Job Statistics¶
Bareos catalog contains lot of information about your IT infrastructure, how many files, their size, the number of video or music files etc. Using Bareos catalog during the day to get them permit to save resources on your servers.
In this chapter, you will find tips and information to measure Bareos efficiency and report statistics.
If you want to have statistics on your backups to provide some Service Level Agreement indicators, you could use a few SQL queries on the Job table to report how many:
- jobs have run
- jobs have been successful
- files have been backed up
- …
However, these statistics are accurate only if your job retention is greater than your statistics period. Ie, if jobs are purged from the catalog, you won’t be able to use them.
Now, you can use the update stats [days=num] console command to fill the JobHistory table with new Job records. If you want to be sure to take in account only good jobs, ie if one of your important job has failed but you have fixed the problem and restarted it on time, you probably want to delete the first bad job record and keep only the successful one. For that simply let your staff do the job, and update JobHistory table after two or three days depending on your organization using the [days=num] option.
These statistics records aren’t used for restoring, but mainly for capacity planning, billings, etc.
The Statistics Retention (Dir->Director) defines the length of time that Bareos will keep statistics job records in the Catalog database after the Job End time. This information is stored in the JobHistory table. When this time period expires, and if user runs prune stats command, Bareos will prune (remove) Job records that are older than the specified period.
You can use the following Job resource in your nightly BackupCatalog (Dir->Job) job to maintain statistics.
PostgreSQL Database¶
Compacting Your PostgreSQL Database¶
Over time, as noted above, your database will tend to grow until Bareos starts deleting old expired records based on retention periods. After that starts, it is expected that the database size remains constant, provided that the amount of clients and files being backed up is constant.
Note that PostgreSQL uses multiversion concurrency control (MVCC), so that an UPDATE or DELETE of a row does not immediately remove the old version of the row. Space occupied by outdated or deleted row versions is only reclaimed for reuse by new rows when running VACUUM. Such outdated or deleted row versions are also referred to as dead tuples.
Since PostgreSQL Version 8.3, autovacuum is enabled by default, so that setting up a cron job to run VACUUM is not necesary in most of the cases. Note that there are two variants of VACUUM: standard VACUUM and VACUUM FULL. Standard VACUUM only marks old row versions for reuse, it does not free any allocated disk space to the operating system. Only VACUUM FULL can free up disk space, but it requires exclusive table locks so that it can not be used in parallel with production database operations and temporarily requires up to as much additional disk space that the table being processed occupies.
All database programs have some means of writing the database out in ASCII format and then reloading it. Doing so will re-create the database from scratch producing a compacted result, so below, we show you how you can do this for PostgreSQL.
For a PostgreSQL database, you could write the Bareos database as an ASCII file (bareos.sql) then reload it by doing the following:
pg_dump -c bareos > bareos.sql
cat bareos.sql | psql bareos
rm -f bareos.sql
Depending on the size of your database, this will take more or less time and a fair amount of disk space. For example, you can cd to the location of the Bareos database (typically /var/lib/pgsql/data or possible /usr/local/pgsql/data) and check the size.
Except from special cases PostgreSQL does not need to be dumped/restored to keep the database efficient. A normal process of vacuuming will prevent the database from getting too large. If you want to fine-tweak the database storage, commands such as VACUUM, VACUUM FULL, REINDEX, and CLUSTER exist specifically to keep you from having to do a dump/restore.
More details on this subject can be found in the PostgreSQL documentation. The page http://www.postgresql.org/docs/ contains links to the documentation for all PostgreSQL versions. The section Routine Vacuuming explains how VACUUM works and why it is required, see http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/routine-vacuuming.html for the current PostgreSQL version.
What To Do When The Database Keeps Growing¶
Especially when a high number of files are beeing backed up or when working with high retention periods, it is probable that autovacuuming will not work. When starting to use Bareos with an empty Database, it is normal that the file table and other tables grow, but the growth rate should drop as soon as jobs are deleted by retention or pruning. The file table is usually the largest table in Bareos.
The reason for autovacuuming not beeing triggered is then probably the default setting of autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor = 0.2, the current value can be shown with the following query or looked up in postgresql.conf:
bareos=# show autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor;
autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor
--------------------------------
0.2
(1 row)
In essence, this means that a VACUUM is only triggered when 20% of table size are obsolete. Consequently, the larger the table is, the less frequently VACUUM will be triggered by autovacuum. This make sense because vacuuming has a performance impact. While it is possible to override the autovacuum parameters on a table-by-table basis, it can then still be triggered at any time.
To learn more details about autovacuum see http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/routine-vacuuming.html#AUTOVACUUM
The following example shows how to configure running VACUUM on the file table by using an admin-job in Bareos. The job will be scheduled to run at a time that should not run in parallel with normal backup jobs, here by scheduling it to run after the BackupCatalog job.
First step is to check the amount of dead tuples and if autovacuum triggers VACUUM:
bareos=# SELECT relname, n_dead_tup, last_vacuum, last_autovacuum, last_analyze, last_autoanalyze
FROM pg_stat_user_tables WHERE n_dead_tup > 0 ORDER BY n_dead_tup DESC;
-[ RECORD 1 ]----+------------------------------
relname | file
n_dead_tup | 2955116
last_vacuum |
last_autovacuum |
last_analyze |
last_autoanalyze |
-[ RECORD 2 ]----+------------------------------
relname | log
n_dead_tup | 111298
last_vacuum |
last_autovacuum |
last_analyze |
last_autoanalyze |
-[ RECORD 3 ]----+------------------------------
relname | job
n_dead_tup | 1785
last_vacuum |
last_autovacuum | 2015-01-08 01:13:20.70894+01
last_analyze |
last_autoanalyze | 2014-12-27 18:00:58.639319+01
...
In the above example, the file table has a high number of dead tuples and it has not been vacuumed. Same for the log table, but the dead tuple count is not very high. On the job table autovacuum has been triggered.
Note that the statistics views in PostgreSQL are not persistent, their values are reset on restart of the PostgreSQL service.
To setup a scheduled admin job for vacuuming the file table, the following must be done:
Create a file with the SQL statements for example
/usr/local/lib/bareos/scripts/postgresql_file_table_maintenance.sqlwith the following content:SQL Script for vacuuming the file table on PostgreSQL¶\t \x SELECT relname, n_dead_tup, last_vacuum, last_autovacuum, last_analyze, last_autoanalyze FROM pg_stat_user_tables WHERE relname='file'; VACUUM VERBOSE ANALYZE file; SELECT relname, n_dead_tup, last_vacuum, last_autovacuum, last_analyze, last_autoanalyze FROM pg_stat_user_tables WHERE relname='file'; \t \x SELECT table_name, pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size(table_name)) AS total_sz, pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size(table_name) - pg_relation_size(table_name)) AS idx_sz FROM ( SELECT ('"' || relname || '"' ) AS table_name FROM pg_stat_user_tables WHERE relname != 'batch' ) AS all_tables ORDER BY pg_total_relation_size(table_name) DESC LIMIT 5;
The SELECT statements are for informational purposes only, the final statement shows the total and index disk usage of the 5 largest tables.
Create a shell script that runs the SQL statements, for example
/usr/local/lib/bareos/scripts/postgresql_file_table_maintenance.shwith the following content:SQL Script for vacuuming the file table on PostgreSQL¶#!/bin/sh psql bareos < /usr/local/lib/bareos/scripts/postgresql_file_table_maintenance.sql
As in PostgreSQL only the database owner or a database superuser is allowed to run VACUUM, the script will be run as the
postgresuser. To permit thebareosuser to run the script viasudo, write the following sudo rule to a file by executingvisudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/bareos_postgres_vacuum:sudo rule for allowing bareos to run a script as postgres¶bareos ALL = (postgres) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/lib/bareos/scripts/postgresql_file_table_maintenance.shand make sure that
/etc/sudoersincludes it, usually by the line#includedir /etc/sudoers.dCreate the following admin job in the director configuration
SQL Script for vacuuming the file table on PostgreSQL¶# PostgreSQL file table maintenance job Job { Name = FileTableMaintJob JobDefs = DefaultJob Schedule = "WeeklyCycleAfterBackup" Type = Admin Priority = 20 RunScript { RunsWhen = Before RunsOnClient = no Fail Job On Error = yes Command = "sudo -u postgres /usr/local/lib/bareos/scripts/postgresql_file_table_maintenance.sh" } }
In this example the job will be run by the schedule WeeklyCycleAfterBackup, the
Priorityshould be set to a higher value thanPriorityin the BackupCatalog job.
Repairing Your PostgreSQL Database¶
The same considerations apply as for Repairing Your MySQL Database. Consult the PostgreSQL documents for how to repair the database.
For Bareos specific problems, consider using bareos-dbcheck program.
MySQL/MariaDB¶
MySQL/MariaDB Support¶
As MariaDB is a fork of MySQL, we use MySQL as synonym for MariaDB and fully support it. We test our packages against the preferred MySQL fork that a distribution provides.
Compacting Your MySQL Database¶
Over time, as noted above, your database will tend to grow. Even though Bareos regularly prunes files, MySQL does not automatically reuse the space, and instead continues growing.
It is assumed that you are using the InnoDB database engine (which is the default since MySQL Version 5.5).
It is recommended that you use the OPTIMIZE TABLE and ANALYZE TABLE statements regularly. This is to make sure that all indices are up to date and to recycle space inside the database files.
You can do this via the mysqlcheck command:
mysqlcheck -a -o -A
Please note that the database files are never shrunk by MySQL. If you really need to shrink the database files, you need to recreate the database. This only works if you use per-table tablespaces by setting the innodb_file_per_table configuration option. See http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/innodb-multiple-tablespaces.html for details.
Repairing Your MySQL Database¶
If you find that you are getting errors writing to your MySQL database, or Bareos hangs each time it tries to access the database, you should consider running MySQL’s database check and repair routines.
This can be done by running the mysqlcheck command:
mysqlcheck --all-databases
If the errors you are getting are simply SQL warnings, then you might try running bareos-dbcheck before (or possibly after) using the MySQL database repair program. It can clean up many of the orphaned record problems, and certain other inconsistencies in the Bareos database.
A typical cause of MySQL database problems is if your partition fills. In such a case, you will need to create additional space on the partition.
MySQL Table is Full¶
If you are running into the error The table ’File’ is full …, it is probably because on version 4.x MySQL, the table is limited by default to a maximum size of 4 GB and you have probably run into the limit. The solution can be found at: http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/full-table.html
You can display the maximum length of your table with:
mysql bareos
SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM bareos like "File";
If the column labeled “Max_data_length” is around 4Gb, this is likely to be the source of your problem, and you can modify it with:
mysql bareos
ALTER TABLE File MAX_ROWS=281474976710656;
MySQL Server Has Gone Away¶
If you are having problems with the MySQL server disconnecting or with messages saying that your MySQL server has gone away, then please read the MySQL documentation, which can be found at:
MySQL Temporary Tables¶
When doing backups with large numbers of files, MySQL creates some temporary tables. When these tables are small they can be held in system memory, but as they approach some size, they spool off to disk. The default location for these temp tables is /tmp. Once that space fills up, Bareos daemons such as the Storage daemon doing spooling can get strange errors. E.g.
Fatal error: spool.c:402 Spool data read error.
Fatal error: backup.c:892 Network send error to SD. ERR=Connection reset by
peer
What you need to do is setup MySQL to use a different (larger) temp directory, which can be set in the /etc/my.cnf with these variables set:
tmpdir=/path/to/larger/tmpdir
bdb_tmpdir=/path/to/larger/tmpdir
MySQL: Lock Wait Timeout¶
In large environments, the Bareos MySQL/MariaDB backend may run in a lock wait timeout. This can be seen as Bareos message, e.g.:
In this case the MySQL/MariaDB innodb_lock_wait_timeout must be increased. A value of 300 should be sufficient.
...
[mysqld]
innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 300
...
Backing Up Your Bareos Database¶
If ever the machine on which your Bareos database crashes, and you need to restore from backup tapes, one of your first priorities will probably be to recover the database. Although Bareos will happily backup your catalog database if it is specified in the FileSet, this is not a very good way to do it, because the database will be saved while Bareos is modifying it. Thus the database may be in an instable state. Worse yet, you will backup the database before all the Bareos updates have been applied.
To resolve these problems, you need to backup the database after all the backup jobs have been run. In addition, you will want to make a copy while Bareos is not modifying it. To do so, you can use two scripts provided in the release make_catalog_backup and delete_catalog_backup. These files will be automatically generated along with all the other Bareos scripts. The first script will make an ASCII copy of your Bareos database into bareos.sql in the working directory you specified in your configuration, and the second will delete the bareos.sql file.
The basic sequence of events to make this work correctly is as follows:
- Run all your nightly backups
- After running your nightly backups, run a Catalog backup Job
- The Catalog backup job must be scheduled after your last nightly backup
- You use
Run Before Job (Dir->Job)to create the ASCII backup file andRun After Job (Dir->Job)to clean up
Assuming that you start all your nightly backup jobs at 1:05 am (and that they run one after another), you can do the catalog backup with the following additional Director configuration statements:
It is preferable to write/send the bootstrap file to another computer. It will allow you to quickly recover the database backup should that be necessary. If you do not have a bootstrap file, it is still possible to recover your database backup, but it will be more work and take longer.